CROTON MEMBRANACEUS
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Genus: Croton Species: Croton membranaceus
BOTANICAL DESCRIPTION
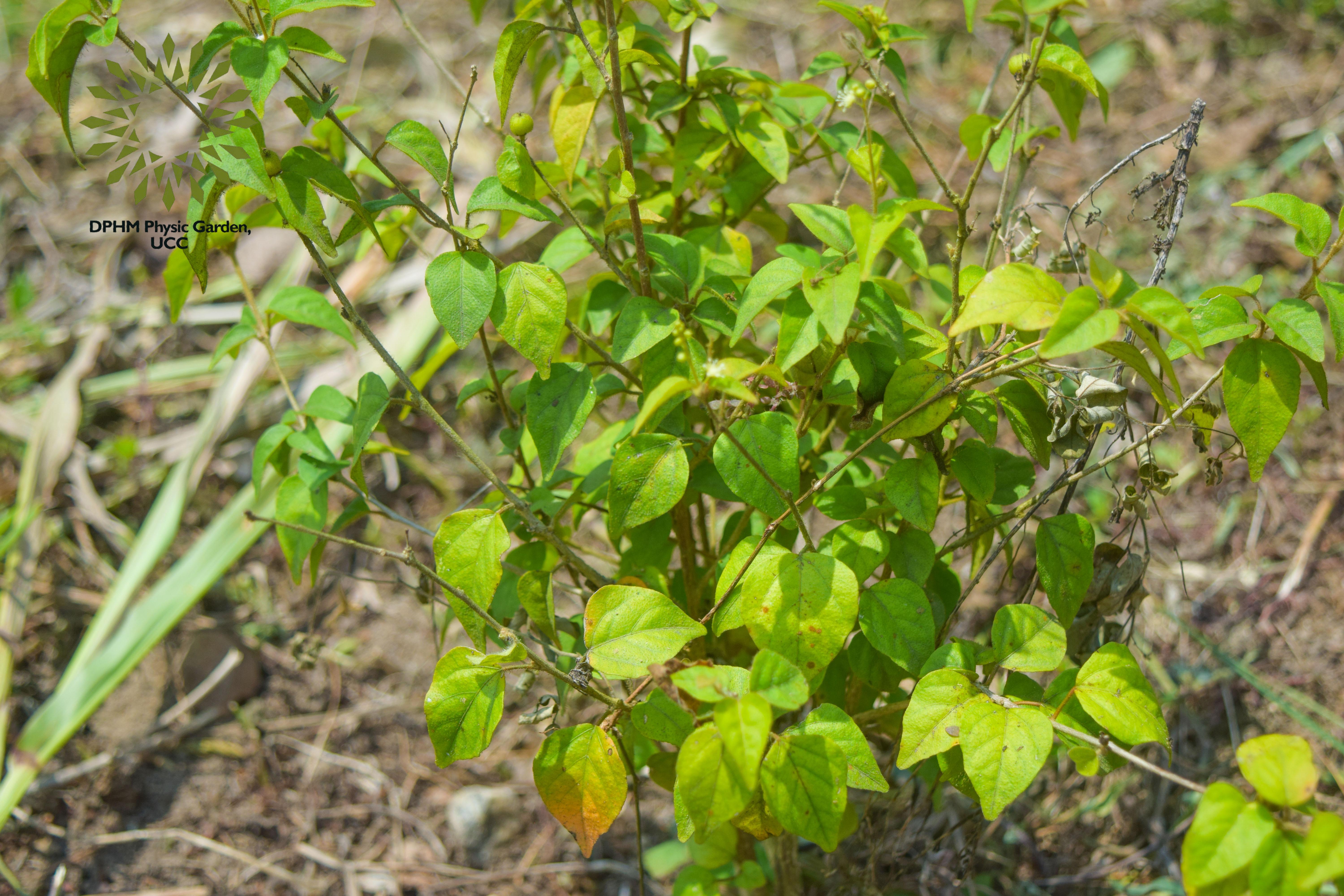
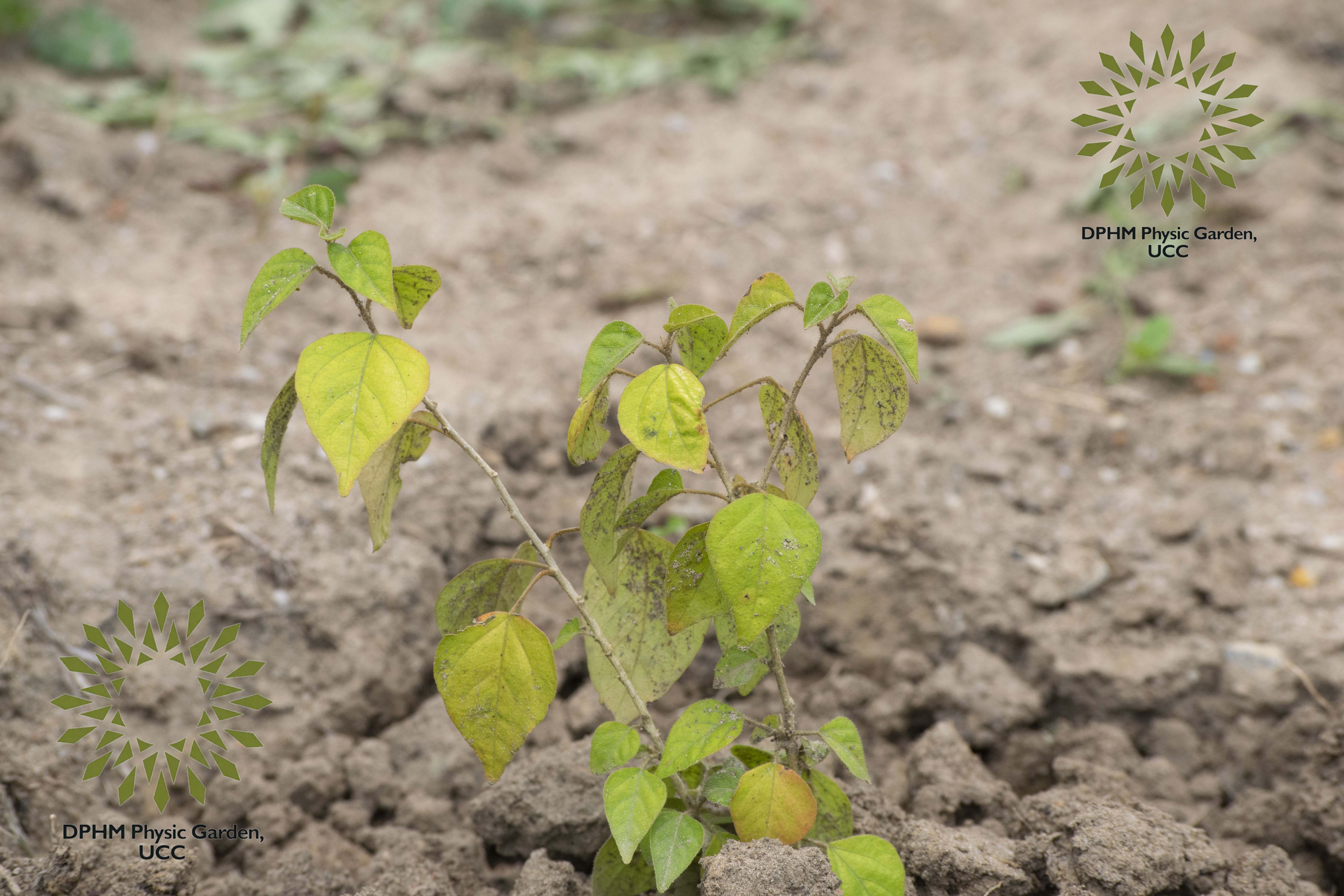
Croton membranaceus is characterized as a shrub. It typically reaches a height of about 1.5 meters. The leaves are alternate, simple, and typically have a glossy appearance. They are often ovate to elliptical in shape, with entire or slightly wavy margins. The leaf surface may exhibit glandular punctuations. The flowers are small and may appear in clusters. They are generally unisexual and can be either male or female, often characterized by a lack of showy petals. The fruit is a capsule that contains seeds, which are dispersed when the capsule dehisces. This species is found in tropical regions, particularly in areas with suitable climatic conditions for shrub growth.
ETHNOBOTANICAL USES
Extracts from the roots and leaves of Croton membranaceus are used in Ghana for benign prostate hyperplasia, in Nigeria to enhance digestion, and in the Bahamas to aromatise tobacco. This plant has several sections that are used to cure various illnesses; in Ghana, however, its root preparations are mostly utilised to treat prostate disorders(Afriyie et al., 2022). In Ghana, formulations for the treatment and management of measles, prostate cancer, and similar conditions employ the root extract of Croton membranaceus. Herbalists and traditional healers in Ghana utilise herbs like Croton membranaceus to cure and/or manage different types of cancer, known as "kokram" in Twi.
PHYTOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Six compounds were isolated from the root extract of Croton membranaceus. These included a new furano-clerodane diterpenoid called "crotomembranafuran" (1), julocrotine, a glutarimide alkaloid, β-sitosterol (3), β-sitosterol-3-β-D-glucoside (4), gomojoside H (5), DL-threitol (6), and β-sitosterol (3). Three of the identified compounds had considerable cytotoxic action against human prostate cancer (PC-3) cells: crotomembranafuran (1), β-sitosterol-3-β-D-glucoside (4), and DL-threitol (6). Gomojoside H (5), julocrotine (2), and crotomembranafuran (1) showed mild inhibitory action against Plasmodium falciparum strain 3D7 in antimalarial testing. It's interesting to note that gomojoside H (5) showed strong antibacterial action against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus, whilst the other compounds showed negligible or no antibacterial activity. Julocrotin (1), a glutarimide alkaloid derived from Croton membranaceus, is isolated, and its spectrum properties are described.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES
Croton membranaceus has been reported to possess various pharmacological activities, including hyperglycemic effects, anti-lipidemic properties, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and potential benefits for cardiovascular health. However, these areas have been less studied, with limited information available. The most extensively researched pharmacological activity of Croton membranaceus is its anticancer effects, particularly in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer.
ANTICANCER ACTIVITY
The aqueous root extract of Croton membranaceus reduced prostate volume and prostatic index (PI) in treated rats at doses of 30 mg/kg body weight (low dose, LD) and 300 mg/kg body weight (high dose, HD). These effects were similar to those observed with finasteride, a standard treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). CMARE specifically targets the prostate, and exerts its effects in a dose-dependent manner by modulating the prostate epithelium and stroma. However, C. Membranaceus root extract has demonstrated cytotoxic activities against DLD-1 (colorectal cancer) and MCF-7 (breast cancer) cells, with IC₅₀ values of 16.0 µg/mL and 17.4 µg/mL, respectively. Induction of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis of BPH-1 cells may be a possible mechanism of action of CMARE. The cytotoxic activity of C. Membranaceus root extract was primarily concentrated in the ethyl acetate fraction, from which six compounds were isolated: a new furano-clerodane diterpenoid, the known glutarimide alkaloid julocrotine, β-sitosterol, β-sitosterol-3-O-glucoside, the labdane diterpenoid gomojoside H, and DL-butane-1,2,3,4-tetraol (DL-threitol).
ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
The stem extracts of Croton membranaceus demonstrated antioxidants through the ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals, indicating significant radical scavenging potential. By reducing oxidative stress, these compounds may help mitigate damage associated with various diseases, highlighting the plant's therapeutic potential. The maximum activity is shown by the ethanolic and ethyl acetate fractions, indicating their potential to help prevent oxidative stress-related disorders such benign prostatic hyperplasia.
DRUG- DRUG INTERACTION OF CROTON MEMBRANACEUS
There is limited information about possible drug drug or drug food interaction between Croton membraneceous and other traditional herbs or synthetic drugs or foods.
POTENTIAL ANTICANCER ABILITY WITH ENZALUTAMIDE
An investigation into the anticancer effect of hydroethanolic root extracts of Croton membraneceous using the 22Rv1 in vitro model of CRPC has revealed a synergistic ability between enzalutamide and Croton membraneceous as a potential anticancer activity. According to the study, the medications enzalutamide and Croton membraneceous together prevent 22Rv1 cells from proliferating, which helps treat cancer. However, the precise mechanism underlying this was not explained.
INTERACTION WITH ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS
This research investigated the potential interaction between extracts from Croton membranaceus and antidiabetic drugs such as metformin and glibenclamide, and in the study the extracts affect the activities of the antidiabetic drugs indicating the potential ability to induce hypoglycemia.
TOXICOLOGICAL PROFILE
A study found that rats given large doses of Croton membranaceus aqueous extract showed no acute toxicity, but decreased creatine kinase levels and enhanced liver enzyme γ-GT. The findings suggest further research on Croton membranaceus' potential impact on liver and muscle function.. The acute toxicity study of Croton membranaceus' aqueous stem extract (CMASE) in male Sprague-Dawley rats revealed an oral LD50 greater than 5000 mg/kg, indicating a relatively safe profile, with no clinical signs of toxicity or death observed. With an LD50 value more than 5 g/kg, the aqueous stem extract Croton membranaceus proved to be rather safe in experiments on the acute and sub-chronic toxicity of male Sprague-Dawley rats.
CLINICAL VALIDATED USES
At the moment, the root extract is being utilised with some success at the Centre for Scientific Research into Plant Medicine (CSRPM), Mampong-Akwapem, for the treatment and management of prostate enlargement as well as prostate and other malignancies, in a variety of dose forms.
REFERENCE
Aboagye, F. A., Sam, G. H., Massiot, G., & Lavaud, C. (2000). Julocrotine, a glutarimide alkaloid from Croton membranaceus. Fitoterapia, 71(4), 461–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00141-6
Afriyie, D. K. (2020). PHARMACOLOGICAL AND TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF STEM EXTRACTS OF CROTON MEMBRANACEUS IN BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA AND PROSTATE CANCER MODELS. UNIVERSITY OF CAPE COAST.
Afriyie, D. K., Ameyaw, E. O., Henneh, I. T., Asare, G., Ofori-Atta, E., Amponsah, S. K., & Appiah-Opong, R. (2024). Acute Oral Toxicological Profile of Croton membranaceus Mull. Arg. Aqueous Stem Extract, a Herbal Treatment for Benign Prostate Hyperplasia, in Male Sprague–Dawley Rats. Journal of Toxicology, 2024, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/7526701
Afriyie, D. K., Asare, G. A., Bugyei, K., Adjei, S., Lin, J., Peng, J., & Hong, Z. (2014a). Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with Croton membranaceus in an experimental animal model. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 157, 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.007
Afriyie, D. K., Asare, G. A., Bugyei, K., Adjei, S., Lin, J., Peng, J., & Hong, Z. (2014b). Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with Croton membranaceus in an experimental animal model. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 157, 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.007
Afriyie, D. K., Asare, G. A., Bugyei, K., Adjei, S., Lin, J., Peng, J., & Hong, Z. (2014c). Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with Croton membranaceus in an experimental animal model. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 157, 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.007
Afriyie, D. K., Asare, G. A., Bugyei, K., Asiedu-Gyekye, I. J., Tackie, R., & Adjei, S. (2014). Prostate-specific targeting of the aqueous root extract of Croton membranaceus in experimental animals. Andrologia, 46(7), 753–760. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12144
Afriyie, D. K., Asare, G. A., Bugyei, K., Lin, J., Peng, J., & Hong, Z. (2015). Mitochondria-dependent apoptogenic activity of the aqueous root extract of Croton membranaceus against human BPH-1 cells. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14(1), 149–162. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.January.15.18
Afriyie, D. K., Ofori Ameyaw, E., Acheampong, D. O., Tuffour, I., & Appiah-Opong, R. (2022). IN-VITRO AND IN-VIVO ANTIOXIDANT PROPERTIES OF STEM EXTRACTS OF CROTON MEMBRANACEUS. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 13(2).
Asare, G. A. (2015a). Croton membranaceus Improves Some Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes in Genetic Animal Models. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/14844.6899
Asare, G. A. (2015b). Croton membranaceus Improves Some Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes in Genetic Animal Models. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/14844.6899
Asare, G. A., Afriyie, D., Ngala, R. A., Appiah, A. A., Anang, Y., Musah, I., Adjei, S., Bamfo-Quaicoe, K., Sule, D., Gyan, B. A., Arhin, P., & Edoh, D. A. (2015). Shrinkage of Prostate and Improved Quality of Life: Management of BPH Patients with Croton membranaceus Ethanolic Root Extract. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/365205
Asare, G. A., Sittie, A., Bugyei, K., Gyan, B. A., Adjei, S., Addo, P., Wiredu, E. K., Nyarko, A. K., Otu-Nyarko, L. S., & Adjei, D. N. (2011a). Acute toxicity studies of Croton membranaceus root extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 134(3), 938–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.02.004
Asare, G. A., Sittie, A., Bugyei, K., Gyan, B. A., Adjei, S., Addo, P., Wiredu, E. K., Nyarko, A. K., Otu-Nyarko, L. S., & Adjei, D. N. (2011b). Acute toxicity studies of Croton membranaceus root extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 134(3), 938–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.02.004
Bayor, M. T. (2007). The Anticancer and Other Bioacttvity Investigations on the Extract and Some Compounds of Croton Membranaceus [Euphorbiaceae] [Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi]. https://ir.knust.edu.gh/handle/123456789/859
Bayor, M. T., Ayim, J. S. K., Marston, G., Phillips, R. M., Shnyder, S. D., Wheelhouse, R. T., & Wright, C. W. (2008a). A Cytotoxic Diterpenoid from Croton Membranaceus , the Major Constituent of Anticancer Herbal Formulations Used in Ghana. Natural Product Communications, 3(11), 1934578X0800301. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X0800301116
Bayor, M. T., Ayim, J. S. K., Marston, G., Phillips, R. M., Shnyder, S. D., Wheelhouse, R. T., & Wright, C. W. (2008b). A Cytotoxic Diterpenoid from Croton Membranaceus , the Major Constituent of Anticancer Herbal Formulations Used in Ghana. Natural Product Communications, 3(11), 1934578X0800301. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X0800301116
De Paula, F. C., Kakazu, S., De Paula, C. B. C., Gomez, J. G. C., & Contiero, J. (2017). Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from crude glycerol by newly isolated Pandoraea sp. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 29(2), 166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.07.002
Fern, K., Ajna, F., & Morris, R. (2014). Useful Tropical Plants Database. Https://Tropical.Theferns.Info/. http://www.prota.org/
https://powo.science.kew.org/. (2023). Croton membranaceus Müll.Arg.
Mshana, N., Abbiw, D., & Addae-Mensah, I. (2000). Traditional medicine and pharmacopoeia: Contribution to the revision of ethnobotanical and floristic studies in Ghana. E., Ahyi, MRA, Enow-Orock, EG, Gbile, ZO, Noamesi,, BK, Odei, MA, Adunlami, H., Oteng-Yeboah, AA, Sarpong, K., Sofowora, A. and Tackie, AN, 290–293.
Sarkodie, J. A., Appiah, A. A., Edoh, D. A., Aboagye, F. A., Asiedu-Larbi, J., Tandoh, M., & Donkor, K. (2013). ANTIHYPERGLYCAEMIC AND ANTIOXIDANT EFFECTS OF CROTON MEMBRANACEUS MULL. ARG (EUPHORBIACEAE). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 5.
Yeboah, K. O., Emosİvbe, M., Ntİm, E. A., Sam, G. H., & Aİnooson, G. (2023). The antiproliferative, antimigratory and anticlonogenic effects of croton membranaceus m?ll. Arg. (Euphorbiaceae) hydroethanolic root extract in human 22rv1 castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. ACTA Pharmaceutica Sciencia, 61(2), 121. https://doi.org/10.23893/1307-2080.APS6109


INFORMATION, DATA AND PICTURES ARE COPYRIGHT OF DPHM, SCHOOL OF PHARMACY, UCC.