DIODIA SCANDENS
BOTANICAL DESCRIPTION
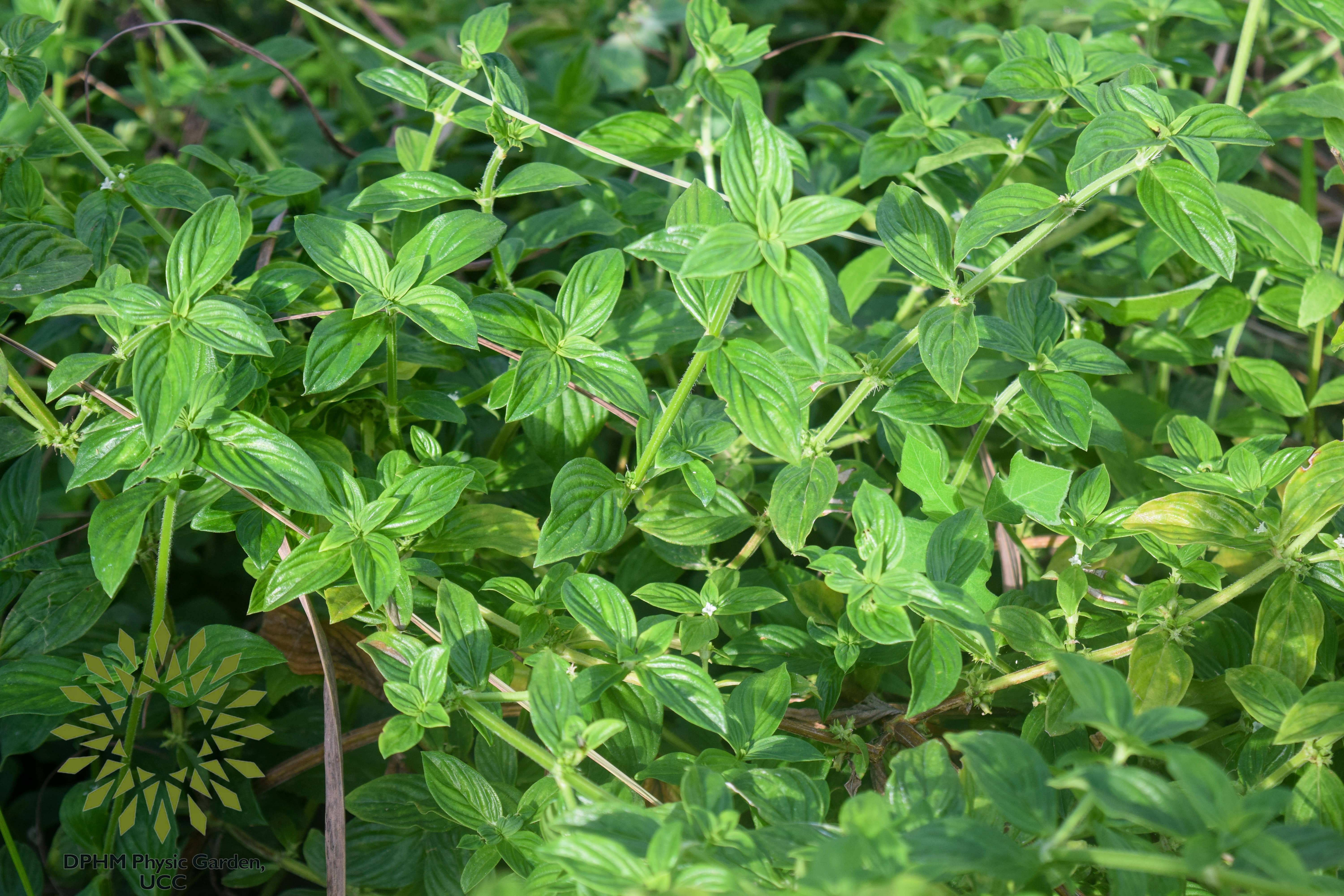
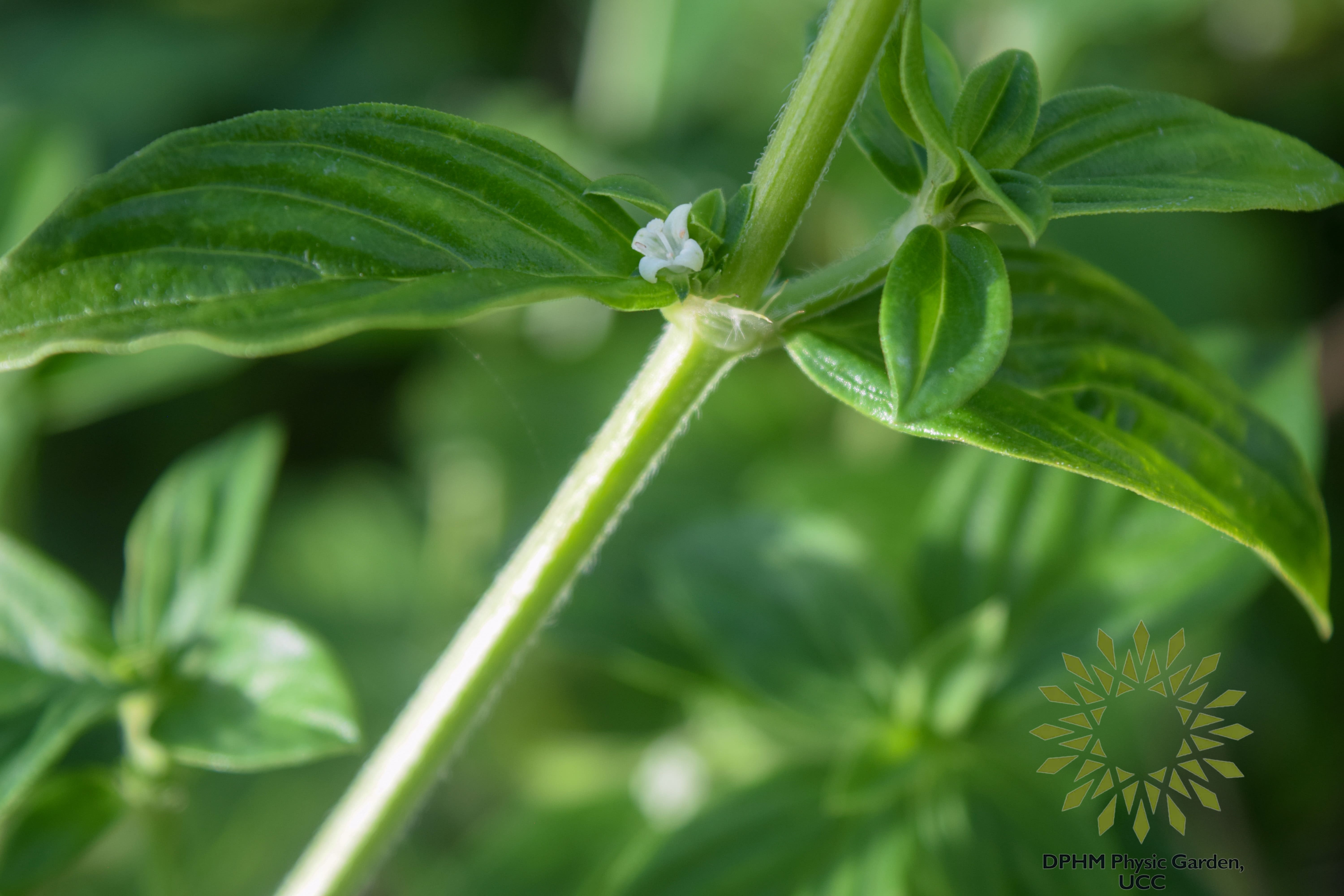
Diodia Scansens Sw (Rubiaceae) is a perennial plant that is evergreen and has alternating leaf arrangement. It also has a petiole. Its compound leaves have a cuneate base, an acute apex, an entire edge, a glabrous surface, and a chartaceous texture. The leaves are ovate to lanceolate in shape. Diodia scandens Sw has a single inflorescence, is odorless and tasteless, and is colored a dark green. The West African medical system has been using this wandering herb for a while. It's really important and helpful. The entire plant is beneficial for treating a variety of illnesses.
TAXONOMY
Family: Rubiaceae
Order: Gentianales Genus: Hexasepalum Bartl.
COMMON NAMES
Itching grass
ETHNOBOTANICAL USES
Diodia scandens is a herb with a taproot and slender stem, used in various countries like Nigeria, Ghana, and the Congo to treat a wide range of health issues, including gout, infections, earaches, epilepsy, wounds, and hypertension. It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-abortifacient properties, helps with snake bites, and is also used for postpartum care, jaundice, diabetes, and more. In Nigeria, it is considered an aphrodisiac and is used to aid childbirth.
PHYTOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES
The phytochemical screening of the leaf extract revealed the presence of saponins, tannins, cardiac glycosides and absence of flavonoids, phlobatannins, alkaloids and anthraquinones. The crude extract of ethyl acetate showed saponin and steroids. The column chromatographic fraction CHDS11 was octadecadienioc acid, while CHDS12 was 1, 2, 3-propanetriyltris. The presence of these chemicals justified the plant's potential use for arthritis treatment. The phytochemicals present in D. scandens include saponin (6.58%), tannin (2.27 mg/100g), alkaloids (10.53%) and phytin phosphorus (1.80 mg/g). Other phytochemicals also present in qualitative tests of the phytochemicals include flavonoids, essential oils, phenols, polyphenol, phytate, phytin phosphorus and oxalate, steroidal and cardiac glycoside.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES
ANALGESIC AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY
The aqueous leaf extract of Diodia scandens showed anti-inflammatory properties in an acute inflammation model, significantly reducing paw edema. The extract, combined with carrageenan and egg-white, inhibited certain inflammation mediators, as measured immediately and 3 hours post-administration. Moreover, the petroleum ether extract of Diodia scandens significantly protected rats from ulcers induced by aspirin, indomethacin, and reserpine in a dose-dependent manner. It also increased the pain threshold in mice.
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITIES
The ethanol extract of Diodia scandens demonstrated strong antibacterial potential, effectively inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus from patient wounds and burns with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 200 µg/mL, and showing a continuous logarithmic reduction in viable cell counts over a 6-hour interval. Additionally, the aqueous leaf extract significantly inhibited in vitro sporulation and mycelial growth of Colletotrichum destructivum, a pathogen affecting cowpea, with greater effectiveness compared to the standard fungicide benomyl. The extract also showed antifungal activity against Microsoptium gypseum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Trichophyton rubrum with MIC and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) values of 6.25/12.5 mg/mL, 3.13/6.25 mg/mL, and 3.13/6.25 mg/mL, respectively.
ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
The study evaluated the antioxidant properties of Diodia scandens extracts using DPPH, thiobarbituric acid, and total antioxidant capacity assays. Results showed significant antioxidant activity in the aqueous extract, with lower IC50 values than ascorbic acid. The aqueous extract showed higher ascorbic acid equivalent values.
ANTIMALARIAL ACTIVITY
A study on Diodia scandens leaf extracts showed significant anti-plasmodial activity against a Congolese Plasmodium falciparum strain. The extracts inhibited the parasite's growth, with IC50 values below 5 μg/mL. The findings suggest Diodia scandens as a promising candidate for antimalarial therapies.
ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY
The n-hexane leaf extract of Diodia scandens significantly reduced blood glucose levels in diabetic rats by the 7th day, indicating its potential as an antidiabetic agent, indicating its potential for further research in natural diabetes treatments.
CLINICAL VALIDATED USES
Not reported
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTION
Not reported
TOXICITY STUDIES
Diodia scandens, an extract with an LD50 of over 5000 mg/kg, showed no significant changes in biochemical markers, body weights, organ weights, or histological examinations in acute and chronic toxicity studies. A slightly higher LD50 of 1342.32 mg/kg was found in another study.
CLINICAL VALIDATED USES
Mist Diodia is an herbal-based therapy used at Centre for Plant Medicine Research (CPMR), Mampong-Akuapem for more than two decades, for the management of Hypertension. It is composed of aqueous leaf extract of Diodia scandens.
REFERENCES
Akpuaka, M. U., Chime, J. C., & Igoli, J. O. (2018a). Phytochemical Analysis of n- Hexane and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Diodia scandens Sw and Spectroscopic Identification of an Omega- 6 Fatty Acid and a Glyceryl Trilinoleoate. Physical Science International Journal, 19(3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.9734/PSIJ/2018/42782
Akpuaka, M. U., Chime, J. C., & Igoli, J. O. (2018b). Phytochemical Analysis of n-Hexane and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Diodia scandens Sw and Spectroscopic Identification of an Omega-6 Fatty Acid and a Glyceryl Trilinoleoate. Physical Science International Journal, 19(3), 1–9.
Asiedu-Larbi, J., Adjimani, J. B., Okine, L. K. N., Nyarko, A. K., & Ocloo, A. (2020a). ACUTE AND CHRONIC TOXICITY STUDIES OF THE AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF MIST DIODIA, ITS CONTRIBUTING PLANTS: Diodia scandens AND Aframomum melegueta IN MALE AND FEMALE SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS. Journal of Global Biosciences, 9(10), 7988–8013.
Asiedu-Larbi, J., Adjimani, J., Okine, L., Nyarko, A., & Ocloo, A. (2020b). Acute and chronic toxicity studies of the aqueous extract of mist Diodia, its contributing plants: Diodia scandens and Aframomum melegueta in male and female sprague-dawley rats. Journal of Global Biosciences, 9, 7988–8013.
Boakye-Yiadom, M., Abrokwa, D. O., Sapaty, C., Yeboah, R., & Ocloo, A. (2016). Retrospectivestudy on Mist Diodia as an Antihypertensive.
Boakye-Yiadom, M., Ronald, D. O. A. C. S., & Ocloo, Y. A. (2016). Retrospectivestudy on Mist Diodia as an Antihypertensive. J Nat Sci Res, 6(24), 37–41.
Burkill, H. M. (1994). The useful plants of West Tropical Africa. Vol. 2: Families EI. (Issue Ed. 2).
Chinedu, O. H., Emenike, A. F., & Augusta, A. E. (2020). Phytochemical and antioxidant properties of Diodia sarmentosa swartz leaves. Mongolian Journal of Chemistry, 21(47), 27–32.
Essiett, U., Bala, D., & Agbakahi, J. (2010a). Pharmacognostic studies of the leaves and stem of Diodia scandens Sw in Nigeria.
Essiett, U., Bala, D., & Agbakahi, J. (2010b). Pharmacognostic studies of the leaves and stem of Diodia scandens Sw in Nigeria.
Essiett, U., Bala, D., & Agbakahi, J. (2010c). Pharmacognostic studies of the leaves and stem of Diodia scandens Sw in Nigeria.
Memvanga, P. B., Tona, G. L., Mesia, G. K., Lusakibanza, M. M., & Cimanga, R. K. (2015). Antimalarial activity of medicinal plants from the Democratic Republic of Congo: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 169, 76–98.
Mittal, G., Aguwa, C., Ezeiru, V., & Akubue, P. (1981). Preliminary pharmacological studies on antivenom action of Diodia scandens leaves. Nigerian Journal of Pharmacy, 12, 432–436.
NA, E., Okezie-Okoye, C., & Abo, K. (2020). Antidiabetic Potentials of Diodia sarmentosa SW (Rubiaceae) Leaves on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats.
Ogu, G., Madagwu, E., Eboh, O., & Ezeadila, J. (2011). Anti-fungal evaluation of Diodia scandens SW leaf extracts against some dermatophytes in Ukwuani Region of Delta State, Nigeria. Int Res J Plant Sci, 2(10), 311–316.
Ojo, S. K., Osanyinlusi, S. A., Jeje, T. O., & Esumeh, F. I. (2017a). Phytochemical and antibacterial properties of Diodia scandens and Phyllanthus amarus on staphylococci isolated from patients in tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Journal of Medicinal Plants for Economic Development, 1(1), 1–6.
Ojo, S. K., Osanyinlusi, S. A., Jeje, T. O., & Esumeh, F. I. (2017b). Phytochemical and antibacterial properties of Diodia scandens and Phyllanthus amarus on staphylococci isolated from patients in tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Journal of Medicinal Plants for Economic Development, 1(1), 1–6.
Ojo, S. K., Osanyinlusi, S. A., Jeje, T. O., & Esumeh, F. I. (2017c). Phytochemical and antibacterial properties of Diodia scandens and Phyllanthus amarus on staphylococci isolated from patients in tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Journal of Medicinal Plants for Economic Development, 1(1), 1–6.
Okokon, J. E., Udoh, A. E., Frank, S. G., & Amazu, L. U. (2012). Anti–inflammatory and analgesic activities of Melanthera scandens. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2(2), 144–148.
Sa, S. (2019). Analysis of Phytoconstituents of Desmodium Adscendens in Relation to its Therapeutic Properties. American Journal of Biomedical Science & Research, 2(4). https://doi.org/10.34297/AJBSR.2019.02.000598
Sadiq Wada, A., Julde, S. M., Borodo, S. B., Ahmad, M. H., Malami, S., & Yaro, A. H. (2022). Phytochemistry, ethnomedicinal uses and pharmacological activity of Diodia scandens ; a review of current scientific literature. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 9(1), 533–541. https://doi.org/10.1080/2314808X.2022.2098462
Van Vuuren, S. (2008). Antimicrobial activity of South African medicinal plants. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 119(3), 462–472.
INFORMATION, DATA AND PICTURES ARE COPYRIGHT OF DPHM, SCHOOL OF PHARMACY, UCC.