SPONDIAS MOMBIN
BOTANICAL DESCRIPTION
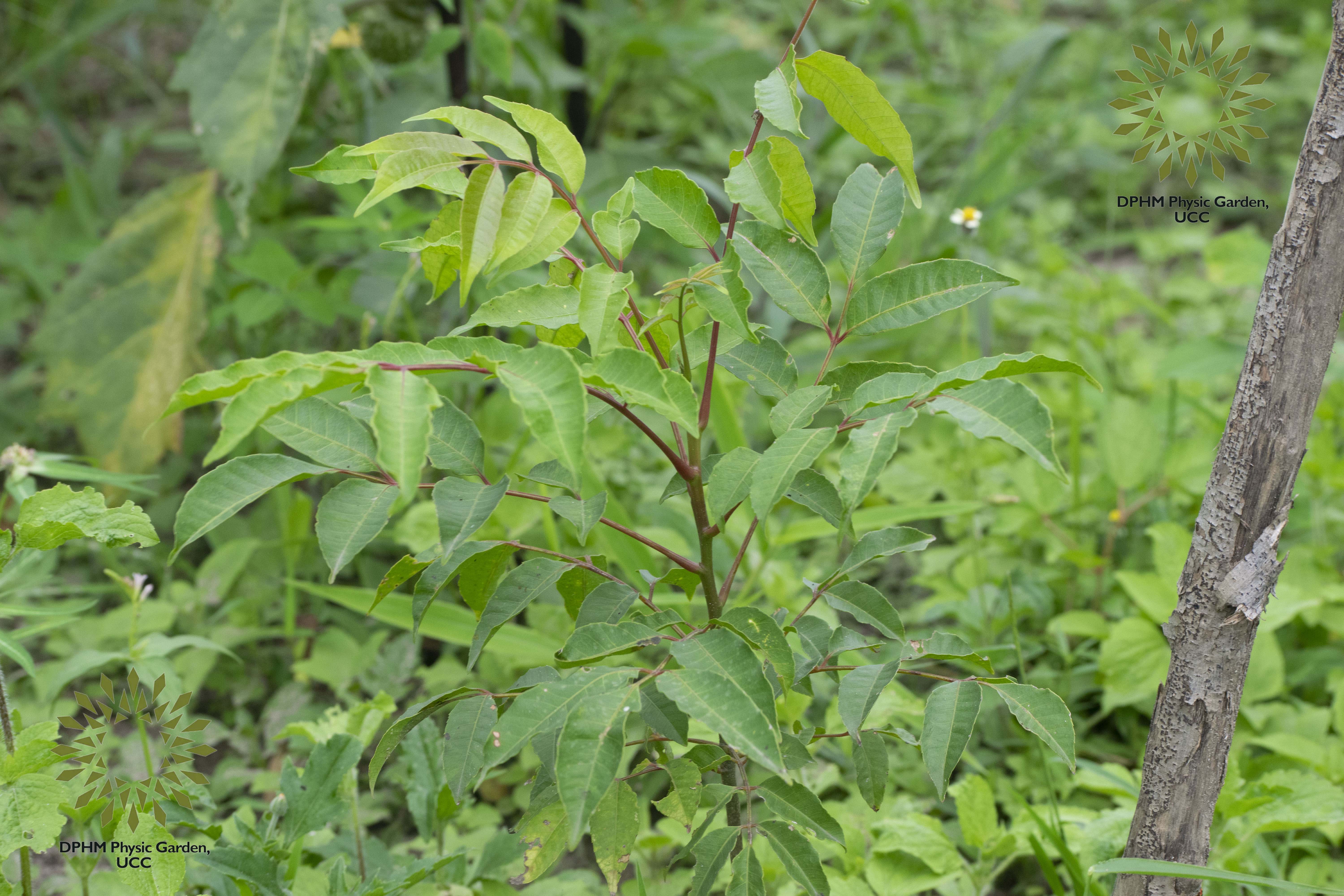
The tropical tree may reach heights of 20–30 m with a trunk diameter of 60–75 cm when it grows upright and has thick, rough bark. The tree's leaves are 20–45 cm long, hairy underneath, and have five to eleven pairs of petiolate leaflets and short petioles. Its blooms are typically white and produced in large, fragrant panicles. The midrib has a bulging symmetry with supporting vascular bundles in a closed arc shape, and the leaf's tetracytic/anomocytic stomata are dispersed on the dorsal or abaxial surface. The fruits have a luscious flesh and are 2-4 cm in length and 2.5 cm in breadth. They have thin, rough skin. Depending on the carotenoid content, these fruits are often green when they first appear and become golden-yellow when mature. The endocarp, a pentagonal structure coated in tubercles, contains the noticeably large and gritty seeds. The parenchymatous and the locular mass are responsible for the endocarp's unique appearance as the most noticeable fruit component. Because it is thin and starchy, the endosperm adheres to the interior surface of the tegument.
TAXONOMY
Family: Anacardiaceae Subfamily: Spondiadoideae
Genus: Spondias Species: Spondias mombin
SYNONYMS
Spondias lutea
LOCAL NAME
Akukor and Atoa (TWI)
Isada(Hausa)
Akukor(Ewe)
Ataaba(Fante)
Aadon(Ga)
COMMON NAMES
Golden Apple, Hog-Plum Tree and Yellow Mombin
ETHNOBOTANICAL USES
S. mombin has a frequent rate of ethnomedicinal utility in cases of abortion, constipation, fever, gonorrhea, postpartum hemorrhage, digestive pain, diarrhea, dysentery and wounds. Spondias mombin Linn (SM) has been used in ethnomedicines in the treatment of diseases including viral diseases. It is also a well-known febrifuge, treats spasms, relieves stomach cramps and reduces pain during childbirth.
PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING
HPLC-DAD analysis identified phenolic components ellagic acid and chlorogenic acid in S. mombin leaf hydroethanolic extract, along with flavonoids, tannins, and triterpenes as additional phytochemicals. Yellow mombin juice, analyzed using HPLC, showed high levels of epicatechin and quercetin, as well as geraniin and chlorogenic acid, bioactive phenols. The methanol extract of Spondias mombin seed, identified through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, contains dodecanoic acid (22.48%), tetradecanoic acid (17.95%), n-hexadecanoic acid (15.35%), capsaicin (12.11%), and dihydrocapsaicin (5.23%). This plant produces an abundance of carotenoids in its leaves, including astaxanthin, β-carotene-15,15'-epoxide, and 7,7',8,8'-tetrahydro-β, β-carotene. Phytochemical screening of Spondias mombin crude leaf extracts revealed the presence of various bioactive compounds with potential antiviral properties, including d-Limonene, p-Cymene, Thymol, and Carvacrol. The phytochemical screening of Spondias mombin revealed the presence of the anthelmintic compound phaeophorbide-a, which was isolated from the leaf extract. Seven compounds; gallic acid (1) (+)-catechin (2), (+)-epicatechin (3), (+)-catechin-5-Ogallate (4), 1-O-gallylglycerol (5), β-sistosterol-D-glucose (6) and β-sistosterol (7) were isolated by phytochemical screening.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin leaves exhibit strong anti-inflammatory properties against carrageenan-induced peritonitis in mice. They contain ellagic acid and chlorogenic acid, potentially acting as antioxidants, suggesting potential use as a natural anti-inflammatory drug. The hydroethanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaf (HESM) demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in a hamster model of oral mucositis caused by 5-fluorouracil, facilitated by suppressing pro-inflammatory indicators and raising glutathione levels. Spondias mombin leaves show anti-inflammatory activity in human neutrophils due to bioactive phenolic compounds like geraniin and chlorogenic acid, supporting traditional use in treating inflammatory conditions.
ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
The hydroethanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaf showed antioxidant activity in oral mucositis, decreasing SOD and MDA levels and increasing GSH. Methanol extract and Spondias mombin leaf fractions exhibit strong antioxidant and anti-denaturation properties, with ether and flavonoid-rich fractions having potent inhibitory effects on lipid peroxidation, metal chelation, and radical scavenging, preserving biomolecules' structural integrity.
ANTI-ULCER AND GASTROPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin L exhibits strong anti-ulcer action in stomach ulcer models, with reduced ulcer area and antioxidant properties when extracted ethanolically. Its antioxidant, cytoprotective, antisecretory, and anti-Helicobacter pylori properties contribute to its anti-ulcer properties. Yellow mombin juice (YMJ) in Wistar rats has strong gastroprotective and ulcer-healing properties, suppressing ulcer development in ethanol- and indomethacin-induced models. Its action is attributed to non-protein sulfhydryl groups, prostaglandins, and reduced stomach acid output. YMJ also stimulates gastric mucosa regeneration, aiding in ulcer repair.
ANTI-TUMOR, ANTI-CANCER AND ANTI-PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin L. stem bark exhibits strong anti-proliferative effects on guinea maize root radicals and cytotoxicity against tadpoles, with potent effects in ethyl acetate and chloroform fractions, possibly due to its phytochemical components. Carotenoids from Spondias mombin leaves show anti-cancer properties in Wistar rats with DMBA-induced breast cancer, targeting XIAP, an important apoptosis regulator, a potential therapeutic target. Mice with liver cancer were treated with an ethanol extract of Spondias mombin leaves, showing anti-cancer properties due to its bioactive substances, including alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, saponins, tannins, phenolic compounds, steroids, flavonoids, and terpenoids.
ANTI- HYPERLIPIDAEMIC ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin leaves contain carotenoids that inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, resulting in anti-lipidemic and anticancer effects, making them a potential natural substitute for treating dyslipidemia and related malignancies. The methanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaves (MESM) has been found to have a strong anti-hyperlipidemic effect in diabetic rats, possibly due to its phytochemicals.
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY
Antimicrobial activity of Spondias mombin extract has been demonstrated against strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Strong in vitro antiviral activity against the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) has been demonstrated by Spondias mombin extract, fractions, and the compound geraniin. Spondias mombin leaf extracts show potential antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, Ebola, and Marburg viruses, with bioactive compounds like d-Limonene, p-Cymene, Thymol, and Carvacrol contributing to their antiviral properties.
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY
The methanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaves (MESM) has been found to have strong antihyperlipidemic and antidiabetic properties in diabetic rats, possibly due to its antioxidant and lipid-regulating properties. Spondias mombin leaves tannins showed antidiabetic benefits in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes, lowering blood glucose levels, restoring amylase activity, and altering body weight, possibly due to altered insulin signaling pathways. Spondias mombin leaf extract showed strong antidiabetic efficacy in diabetic rats, with its chloroform fraction lowering blood glucose levels by 60.6%. Its phytochemicals, including ellagitannins, anacardic acid, and pelargonic acid, may alter insulin sensitivity.
ANTIPYRETIC ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin leaf extract showed strong antipyretic effects in mouse models of yeast-induced hyperthermia and 2,4-dinitrophenol-induced hyperthermia, with maximum effects at 200 mg/kg for 2,4-DNP and 100 mg/kg for yeast fever.
ANALGESIC ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin, with its phytochemical components like tannins, saponins, and anthraquinone glycosides, has shown strong analgesic effects, potentially serving as a substitute for traditional analgesic medications. The methanolic leaf extract of Spondias mombin showed significant peripheral analgesic efficacy in mice, reducing acetic acid-induced writhing and showing no central nervous system effects, suggesting potential natural pain treatment.
OXYTOCIC ACTIVITY
The leaf extract of Spondias mombin showed oxytocic activity, increasing spontaneous uterine contraction frequency and causing abortions in pregnant rats. Spondias mombin leaves, are used for birthing, have hydro-ethanolic extract showing strong oxytocic activity, enhancing uterine smooth muscle contractions through prostaglandin release stimulation, α2-adrenoceptor activation, and calcium release.
HAEMATOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
The aqueous extract of Spondias mombin leaves improved hematological parameters in Ancylostoma caninum-infected dogs by significantly lowering total cholesterol and phospholipids, enhancing packed cell volume, and slightly decreasing white blood cell counts. This plant's traditional use in treating anemia, especially in expectant mothers, is validated.
ANTI-PARASITIC ACTIVITY
Ancylostoma caninum showed significant anthelmintic activity when exposed to Spondias mombin leaves' aqueous extract by reducing fecal eggs and returning faces to their usual consistency.
HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin leaf and stem extracts showed hepatoprotective effects on rats exposed to carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage, indicating the plant's antioxidant properties influence its hepatoprotective action. The methanol extract of Spondias mombin leaf has been found to protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats, possibly due to its antioxidant properties, which reduce oxidative stress and liver damage.
ANTI-MALARIAL ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin Linn. stem bark exhibits potent antimalarial properties, reducing parasitemia and extending life in mice with Plasmodium berghei infection, likely due to its antioxidant-rich phytochemicals. Research shows S. mombin leaf extracts have adulticidal properties against Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, with the dichloromethane fraction being the most efficient for mosquito-killing.
CARDIOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY
The aqueous extract of Spondias mombin demonstrated strong cardioprotective action against isoproterenol-induced myocardial damage in animals, reversing inflammatory indices, antioxidant capacity, and cardiac damage indicators due to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The study found that supplementing rats with Spondias mombin can mitigate cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction, enhancing energy utilization, reducing oxidative stress, and reducing inflammatory processes. Spondias mombin leaf extract reduces oxidative stress in rat hearts due to antioxidant properties of flavonoids and phenolic substances, suggesting potential therapeutic use for ischemic stroke.
NEPHROPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY
Spondias mombin has been found to have nephroprotective properties against aluminum chloride damage in female albino rats, by increasing antioxidant enzyme activities and reducing oxidative damage. Spondias mombin has been found to have nephroprotective properties in Wistar rats, reducing the harmful effects of oxidative stress on kidneys.
NEUROPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY
The leaves of Spondias mombin demonstrate neuroprotective action by reducing oxidative stress and modulating key enzymes related to cognitive function, attributed to its phytochemicals like tannins and flavonoids, which may aid in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease by protecting against cognitive damage from scopolamine. Spondias mombin leaves' Q3G-RF, a potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic fraction, has been found to have neuroprotective effects against dichlorvos-induced toxicity in Wistar rats, suggesting potential therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative disorders.
TOXIC PROFILE
The methanol extract of Spondias mombin seed was found to be nontoxic against the RD cell line and did not cause death in any animals, even at a high dosage of 2000 mg/kg. The extract was found safe for oral acute toxicity tests on mice up to 4000 mg/kg. Intraperitoneally, dosages below 1000 mg/kg caused drowsiness and frequent bowel movements. At 1000 mg/kg, sedation, bowel movements, and abdominal contractions occurred. The median fatal dosage was 707 mg/kg.
Pheophorbide-a, a chemical from Spondias mombin's leaf, has shown anthelmintic action against Haemonchus placei without significant cell damage below 200 μM indicating a favorable safety profile for potential lead development. Lorke's approach was used to investigate the extract's oral median lethal dosage. It was discovered that the extract's LD50 was more than 5000 mg/kg. In mice, the extract was discovered to be essentially non-toxic.
CLINICAL VALIDATED USES
Not reported
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTION
Not reported
REFERENCE
Aba, P. E., Ozioko, I. E., Udem, N. D., & Udem, S. C. (2014). Some biochemical and haematological changes in rats pretreated with aqueous stem bark extract of Lophira lanceolata and intoxicated with paracetamol (acetaminophen). Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, 11(4), 273–277. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2014-0007
Abiodun, O. O., Nnoruka, M. E., & Tijani, R. O. (2020). Phytochemical Constituents, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity Assessment of the Seed of Spondias mombin L. (Anacardiaceae). Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 17(3), 343–348. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.galenos.2020.38801
Adediwura, F.-J., & Kio, A. (2009). Antidiabetic Activity of Spondias mombin Extract in NIDDM Rats. Pharmaceutical Biology, 47(3), 215–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200802462493
Adekoya, O., Iwegbu, P., & Adenubi, O. (2022). Anthelmintic, haematological and antioxidant potential of Spondias mombin L. in young dogs. Journal of Sustainable Veterinary & Allied Sciences, 3(1), 57–65.
Ademosun, A. O., Popoola, T. V., Oboh, G., & Fasakin, O. W. (2022). Parquetina nigrescens and Spondias mombin protects against neurochemical alterations in the scopolamine model of cognitive dysfunction. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 46(11). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14213
Afolabi, C. A., Olamide, O. C., Olubukola, B. O., Tolulope, M. O., & Ebenezer, O. F. (2014). Antidenaturation and antioxidative properties of phytochemical components from Spondias mombin. African Journal of Biochemistry Research, 8(5), 101–110. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBR2014.0769
Agbaje, E. O., Ismail, A. I., & Oguntokun, O. J. (1970). Antimicrobial and antipyretic activities of aqueous leaf extract of Spondias mombin Linn. (Anarcadiaceae). Journal of Medicinal Herbs and Ethnomedicine, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.25081/jmhe.2020.v6.5558
Ajaegbu, E., Danga, S. Y., Chijoke, I., & Okoye, F. C. (2016). Mosquito adulticidal activity of the leaf extracts of Spondias mombin L. against Aedes aegypti L. and isolation of active principles. Journal of Vector Borne Diseases, 53(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-9062.179211
Akinmoladun, A. C., Obuotor, E. M., Barthwal, M. K., Dikshit, M., & Farombi, E. O. (2010). Ramipril-Like Activity of Spondias Mombin Linn Against No-Flow Ischemia and Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rat Heart. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 10(4), 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-010-9089-4
Aratak Marques Taia, T., Felipe Vilela Peres, M., Mendes Moreira De Oliveira, I., Nayara Guimarães Teófilo, M., Correia Stoko, N., Ferreira Alves, S., Torres Blanch, G., Nascente Costa, S. H., Borges, L. L., Marques Cardoso, A., Viera Teixeira, M., Pelli De Oliveira, M. A., & Moura Gomes, C. (2023). Evaluation of the effects of SPONDIAS MOMBIN extract as an alternative antimicrobial drug. Revista de Patologia Tropical / Journal of Tropical Pathology, 52(1), 37–49. https://doi.org/10.5216/rpt.v52i1.73022
Arhoghro Ejovwoke Marcellinus & Enebrayi Nelson Onitsha. (2022). Nephroprotective potential of Spondias mombin against aluminum chloride induced-renal injury in female albino rats. World Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 2(1), 001–010. https://doi.org/10.53346/wjast.2022.2.1.0033
Asuquo, R. O., Ekanem, B. T., Udoh, B. P., Mesembe, E. O., & Ebong, E. P. (2013). Haematinic Potential of Spondias Mombin Leaf Extract in Wistar Rats. 4.
Attemene, S. D., Kouakou, G. S., & Dally, I. L. (2015). Assessment of the analgesic activity of methanolic leaves extract of Spondias mombin Linn (Anarcadiaceae). African Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 4.
Boadu, A., Karpoormath, R., & Nlooto, M. (2024a). Pharmaco-phytochemistry of esters isolated from leaf extracts of Spondias mombin as potential antiviral agents. South African Journal of Science, 120(7/8). https://doi.org/10.17159/sajs.2024/14913
Boadu, A., Karpoormath, R., & Nlooto, M. (2024b). Spondias mombin: Biosafety and GC–MS analysis of anti-viral compounds from crude leaf extracts. Advances in Traditional Medicine, 24(1), 349–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-023-00698-y
Boadu, A., Nlooto, M., & Karpoormath, R. (2022). Spondias mombin: In Silico Screening of 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic Acid, Butyl 2-Methylpropyl Ester (Fragment of Geraniin) as Anti-Marburg virus agent. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.166068546.68447309/v1
Brito, S. A., Barbosa, I. S., De Almeida, C. L. F., De Medeiros, J. W., Silva Neto, J. C., Rolim, L. A., Da Silva, T. G., Ximenes, R. M., Menezes, I. R. A. D., Caldas, G. F. R., & Wanderley, A. G. (2018). Evaluation of gastroprotective and ulcer healing activities of yellow mombin juice from Spondias mombin L. PLOS ONE, 13(11), e0201561. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201561
Brito, S. A., De Almeida, C. L. F., De Santana, T. I., Da Silva Oliveira, A. R., Do Nascimento Figueiredo, J. C. B., Souza, I. T., De Almeida, L. L., Da Silva, M. V., Borges, A. S., De Medeiros, J. W., Da Costa Silva Neto, J., De Cássia Ribeiro Gonçalves, R., Kitagawa, R. R., Sant′Ana, A. E. G., Rolim, L. A., De Menezes, I. R. A., Da Silva, T. G., Caldas, G. F. R., & Wanderley, A. G. (2018). Antiulcer Activity and Potential Mechanism of Action of the Leaves of Spondias mombin L. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2018(1), 1731459. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1731459
Cabral, B., Siqueira, E. M. S., Bitencourt, M. A. O., Lima, M. C. J. S., Lima, A. K., Ortmann, C. F., Chaves, V. C., Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. F., Rocha, H. A. O., Scortecci, K. C., Reginatto, F. H., Giordani, R. B., & Zucolotto, S. M. (2016). Phytochemical study and anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential of Spondias mombin leaves. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia, 26(3), 304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2016.02.002
Eluehike, N., & Onoagbe, I. (2018). Changes in organ and body weight, serum amylase and antidiabetic effects of tannins from Spondias mombin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Metabolic Health, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.4102/jir.v3i1.40
GBOLADE, EDOM, MUHAMMAD, & ogunleye. (2019). ANTI-PROLIFERATIVE AND CYTOTOXIC PROPERTIES OF SPONDIAS MOMBIN L. (ANACARDIACEAE) STEM BARK. Journal of Pharmaceutical & Allied Sciences, Vol. 16(Issue 5), p3146-3154. 9p.
Gobinath, R., Parasuraman, S., Sreeramanan, S., Enugutti, B., & Chinni, S. V. (2022). Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Methanolic Extract of Leaves of Spondias mombin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Frontiers in Physiology, 13, 870399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.870399
Herbal, K. (2020, December 1). TWI NAMES OF SOME PLANTS USED TRADITIONALLY IN GHANA. KENOCH HG HERBAL CLINIC. https://kenochherbal.com/2020/12/01/twi-names-of-some-plants-used-traditionally-in-ghana/
Marcellinus, Ejovwoke Arhoghro, Enebrayi Nelson Onitsha, & Berezi E Peter. (2022). Haematological, hepatic and oxidative stress indices of female Wistar rats treated with ethanolic leaf extract of Spondias mombin. World Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical and Medical Research, 3(2), 010–018. https://doi.org/10.53346/wjapmr.2022.3.2.0037
Metibemu, D. S., Akinloye, O. A., Akamo, A. J., Okoye, J. O., Ojo, D. A., Morifi, E., & Omotuyi, I. O. (2020). Carotenoid isolates of Spondias mombin demonstrate anticancer effects in DMBA‐induced breast cancer in Wistar rats through X‐linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) antagonism and anti‐inflammation. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 44(12). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13523
Metibemu, D. S., Akinloye, O. A., Akamo, A. J., Okoye, J. O., & Omotuyi, I. O. (2021). In-silico HMG-CoA reductase-inhibitory and in-vivo anti-lipidaemic/anticancer effects of carotenoids from Spondias mombin. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 73(10), 1377–1386. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpp/rgab103
Nila, T. S., Khan, M. R. A., Nasrin, N., Mim, I. J., Peya, F. Y., Prapty, A. N., Cruze, L. R. M. D., Rahman, Md. A., Jahan, I., Kumkum, M., Habib, R. S., Tahsin, Md. R., Aktar, F., Aktar, T., Chowdhury, J. A., Kabir, S., Chowdhury, A. A., & Amran, Md. S. (2023). An Assessment of Analgesic & Anti-inflammatory Activity Spondias mombin and Mapping of Variation of Potency under the Light Geographical Contrast Based Phenomenon. Asian Journal of Advanced Research and Reports, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajarr/2023/v17i2464
Nwidu, L. L., Elmorsy, E., Oboma, Y. I., & Carter, W. G. (2018). Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Spondias mombin leaf and stem extracts against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, 13(3), 262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2018.03.006
Nworu, C. S., Akah, P. A., Okoli, C. O., & Okoye, T. C. (2007). Oxytocic Activity of Leaf Extract of Spondias mombin . Pharmaceutical Biology, 45(5), 366–371. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200701214755
Ogedengbe-Olowofoyeku, A. N., Ademola, I. O., Wright, C. W., Idowu, S. O., & Fatokun, A. A. (2021). Anthelmintic activity and non-cytotoxicity of phaeophorbide-a isolated from the leaf of Spondias mombin L. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 280, 114392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114392
Ogunro, O. B., Oyeyinka, B. O., Gyebi, G. A., & Batiha, G. E.-S. (2023). Nutritional benefits, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and toxicity of Spondias mombin Linn: A comprehensive review. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 75, 162–226. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpp/rgac086
Ogunro, O. B., Salawu, A. O., Alotaibi, S. S., Albogami, S. M., Batiha, G. E.-S., & Waard, M. D. (2022). Quercetin-3-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside-Rich Fraction from Spondias mombin Leaves Halted Responses from Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis, and Lipid Peroxidation in the Brain of Dichlorvos-Treated Wistar Rats. Toxics, 10(8), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080477
Ojo, O. B., Olagunju, G. B., Olajide, A. O., Jegede, M. E., Fakorede, A. S., Crown, O. O., Olaleye, M. T., & Akinmoladun, A. C. (2022). Spondias mombin leaf extract ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiohepatorenal oxidative stress in rats. Phytomedicine Plus, 2(1), 100196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100196
Orumwensodia, K. O., Gören, N., & Adhikari, A. (2024). Antimalarial, Antioxidant and in Silico Molecular Docking Activities of Phenolics from Spondias Mombin Linn. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4798090
Orumwensodia, K. O., & Uadia, P. O. (2023). Bioactivity-guided fractionation of antimalarial active extract of Spondias mombin Linn stem bark. Nigerian Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 38(3), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.4314/njbmb.v38i3.2
Pakoussi, T., Mouzou, A. P., Metowogo, K., Aklikokou, K. A., & Gbeassor, M. (2018). How do Spondias mombin L (Anacardiaceae) leaves extract increase uterine smooth muscle contractions to facilitate child birth in parturient women? African Health Sciences, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v18i2.6
Pereira, B. L. B., Rodrigue, A., & Oliveira Arruda, F. C. de. (2020). Spondias mombin L. attenuates ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction associated with oxidative stress and inflammatory modulation. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15419
Silva, T. S. J. D., Soares, A. A., Rocha, T. M., Pimenta, A. T. Á., Miron, D., Silva, R. J. F., Viana, G. S. B., & Leal, L. K. A. M. (Kalyne). (2020). Spondias mombin: Quality control and anti-inflammatory activity in human neutrophils. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 24, 100393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100393
Siqueira, E. M. D. S., Lima, T. L. C., Boff, L., Lima, S. G. M., Lourenço, E. M. G., Ferreira, É. G., Barbosa, E. G., Machado, P. R. L., Farias, K. J. S., Ferreira, L. D. S., Rocha, H. A. D. O., Simões, C. M. O., & Zucolotto, S. M. (2020). Antiviral Potential of Spondias mombin L. Leaves Extract Against Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Replication Using In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Planta Medica, 86(07), 505–515. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1135-9066
Sousa Gomes, M., Diógenes Alves Uchoa Lins, R., Zucolotto Langassner, S. M., Dantas Da Silveira, É. J., Gomes De Carvalho, T., Diniz De Sousa Lopes, M. L., De Souza Araújo, L., Addison Carvalho Xavier De Medeiros, C., Ferreira De Carvalho Leitão, R., Coelho Bernardo Guerra, G., Fernandes De Araújo Junior, R., & Antunes De Araújo, A. (2020). Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of hydroethanolic extract of Spondias mombin leaf in an oral mucositis experimental model. Archives of Oral Biology, 111, 104664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104664
Ubah, C. O., Asuquo, O. R., Oko, G. E., & Eluwa, M. A. (2019). Effects of Methanolic Leaf Extracts of Azadirachta indica and Spondias mombin on the Kidneys Histology of Zidovudine Stress Induced Wistar Rats. Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medical Research, 7(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.9734/JOCAMR/2019/46169
Umar Kura, A., John Edet, G., Ahmad Muhammad, M., & Aliyu Nuru, K. (2024). PHARMACOLOGY OF SPONDIAS MOMBIN IN LIVER CANCER TREATMENT AND TOXICITY EVALUATION. Gadau Journal of Pure and Allied Sciences, 3(1), 41–51. https://doi.org/10.54117/gjpas.v3i1.4
INFORMATION, DATA AND PICTURES ARE COPYRIGHT OF DPHM, SCHOOL OF PHARMACY, UCC.